Forex Trading Malaysia
In this guide we will cover the steps to start forex trading in Malaysia for beginner traders. We will cover the risks that you must know & what precautions you must take while opening your Forex trading account to ensure the safety of your funds.
You can trade Forex in Malaysia by opening an account with a Forex broker that is regulated by Top-tier regulators like FCA, ASIC & CySEC.
6 Steps to Start Forex Trading in Malaysia
Summary Table of Best Forex Brokers for Beginner traders in Malaysia in 2023
|
HotForex is a well regulated forex broker licensed with FCA, FSCA & CySEC. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.1 pips
with Zero Account (plus $7 commission per lot) |
Account Minimum
$5
|
Max. Leverage
1:1000 for forex
|
Open Account
on HotForex |
|
|
FXTM is a well regulated forex broker licensed with FCA, FSCA & CySEC. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 1.9 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
₦10,000
|
Max. Leverage
1:2000 for forex
|
Open Account
on FXTM |
|
|
XM Trading is regulated by CySEC and IFSC of Belize. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.8 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$5
|
Max. Leverage
1:888 for forex
|
Open Account
on XM |
|
|
OctaFX is regulated by CySEC and SVGFSA. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.7 pips
with all Accounts |
Account Minimum
$25
|
Max. Leverage
1:500 for forex
|
Open Account
on OctaFX |
|
|
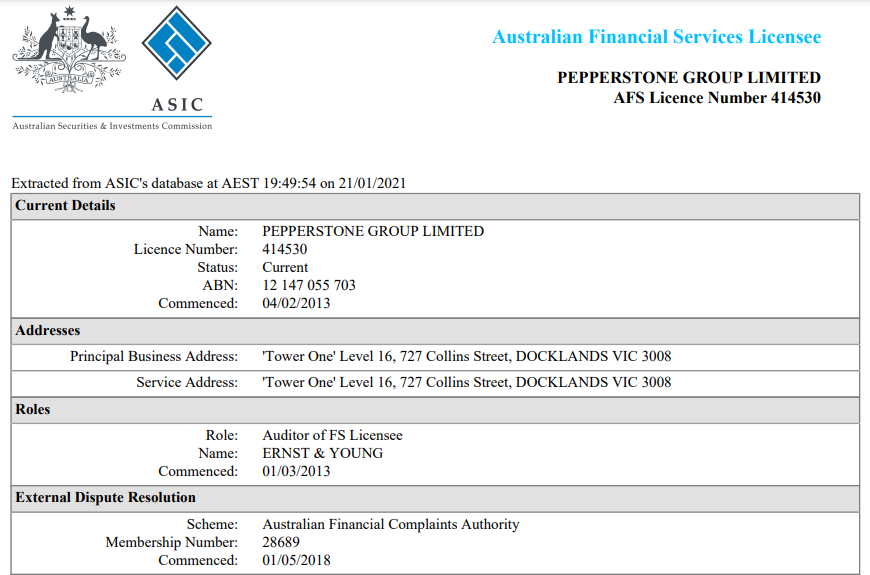
Pepperstone is a well regulated forex broker licensed with FCA, ASIC, CMA & CySEC. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.69 pip
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$0
|
Max. Leverage
1:200 for forex
|
Open Account
on Pepperstone |
The Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, or forex market, serves as a global platform for the exchange of currencies at prevailing rates. It facilitates international transactions by necessitating the exchange of different currencies. To ensure a fair trade, currencies are exchanged based on conversion rates, which vary for each currency pair and are influenced by a multitude of economic and geopolitical factors.
Traders engage in the forex market by analyzing these factors to predict the price movements of currency pairs. Leveraging their insights, they place buy or sell orders through margin trading. However, it’s crucial to recognize that forex trading carries a high level of risk, and many beginners face initial losses.
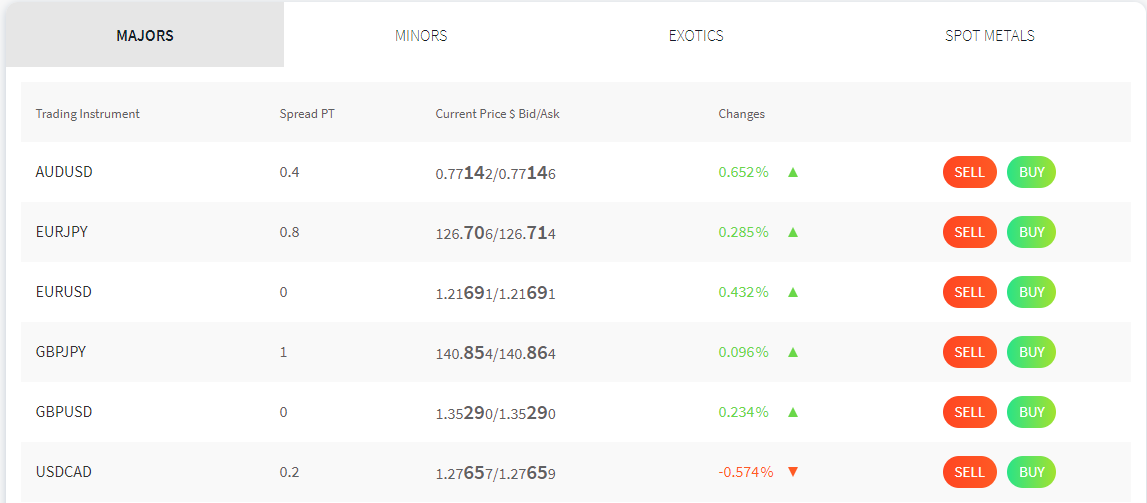
The forex market offers a diverse range of currency pairs, categorized as major, minor, and exotic. The EUR/USD pair is the most heavily traded globally, closely followed by GBP/USD. Trading in any currency pair signifies the exchange of one currency for another, underlining the intricate dynamics of this financial market.
An Example of Currency Exchange
In this example, we shall be using the US dollar (USD) and the Malaysian ringgit (RM).
At the time of this writing, $1 equals RM4.2. So let us say you have $5 at hand. If you speculate as a trader that $1 might equal RM3.5 for some reason, you exchange your $5 for ringgit. Based on the exchange rate, that gives you RM21.
$5 x 4.2/$1= RM21
Now that you have your RM2.1. Let us assume that the exchange rate fell as you speculated. Instead of RM4.2, the exchange rate is now RM3.5 to $1. If you change your RM21 to dollars at this point, you get $6.
RM21x$1/3.5RM=$6
From this calculation, you can see that the RM21 that you got for $5 fetched you $6 because of the change in exchange rate. You made a $1 profit in this trade. This is the simple way forex trading works.
Chapter #1
How Forex is Traded?
Forex trading is like a global market where people trade different currencies. Imagine you have two kinds of money, let’s say dollars and euros. You want to exchange some of your dollars for euros because you think the euro might become more valuable.
So, you go to this big market, and you find someone who wants to trade their euros for your dollars. You agree on a price, make the trade, and now you have euros instead of dollars. If the euro’s value goes up, you can exchange it back for more dollars and make a profit.
But it’s a bit like a game because the values of currencies keep changing all the time. So, you need to be careful and think about when to trade to make money. Forex trading is like playing with money from different countries and trying to win by trading them at the right time.
In this chapter we will cover the various methods how forex is traded.
1) Spot: Spot has one of the shortest transaction time frame in the forex market. It involves cash-to-cash exchange between two currencies. Spot transactions only last for 48 hours and there is no interest involved.
2) Forward: Like spot, forwards also involve direct cash transactions. The difference is just that forward contracts have a flexible transaction time. In a forward transaction, two parties agree to exchange one currency for another at an agreed exchange rate and an agreed date in the future. They exchange the two currencies at the date and exchange rate agreed regardless of the current exchange rate at that time. A forward transaction can last for a few hours to a year.
3) Futures: In futures, there is an exchange of one currency for another at a future date and a future exchange rate. This is the main difference between forwards and futures. In addition, a futures contract can be closed before the expiring date. Forwards cannot be closed before the expiry date.
4) Non-Deliverable Forward: An NDF involves two parties taking the opposite sides of trade over two currencies and an agreed NDF rate. One party buys and the other party sells with an agreement to pay the difference between the agreed rate and the prevailing spot rate at an agreed period. On the agreed date, the difference between the NDF rate and the prevailing spot rate is multiplied by a notional amount.
5) Swap: FX swaps make up 49% of trading activity in April 2019 according to BIS. Two parties exchange a principle amount of two currencies with an agreement to reverse the exchange at a time in the future.
6) Options: In options, a trader holds a currency with the choice to exchange it for another currency at a previously agreed exchange rate at an agreed time. The trader retains the right to carry out the exchange or not.
7) CFDs: CFD means contract for difference. A trader opens a contract to buy or sell a currency pair at an opening price. If the trade goes his way, he is paid the difference between the opening price and the closing price of the contract.
Chapter #2
Understanding Forex Trading with an Example
Understanding forex trading can be complex for those who have never traded on any financial instrument online in the past. Those who have a slight experience of trading other capital markets like stocks, cryptocurrencies, or CFDs would be very comfortable with forex trading.
Let us understand the complete process and working methodology of forex market with the help of an example.
Online forex trading is done through trading platform which is a software that can be downloaded on electronic devices. The trading platform connects the traders to brokers, liquidity providers, and other forex traders.
Traders place buy or sell orders through trading platforms on their preferred trading instruments. The exposure and profit/loss depends on the volume traded and leverage involved.
A leverage of 1:10 will allow you to open a position worth $100 exposure with $10 in your trading account.
In this example, we will take the leverage of 1:10 on EUR/USD currency pair. The supposed market price for EUR/USD is 1.2100/1.2102. This means that the bid price is 1.2100 (the price that the dealer is willing to pay) and the ask price is 1.2102 (the price at which the dealer is willing to buy) and the spread is 2 pips (difference between the bid and ask price at 4th decimal).
First, we will place a buy order for 1 standard lot (100,000 units of the base currency). To place a buy order of 1 standard lot on EUR/USD, the following will be the calculation of the required account balance.
$1.2102 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,102
(ask price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went up by 100 pips and reaches 1.2200/1.2202. By closing the buy position at this price, the following will be the profit.
(1.2200 * 100,000 * 1/10) – $12,102 = $12,200 – $12,102 = $98
(bid price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) – (exposure) = Profit/Loss
Now let us understand the same scenario with a short position on EUR/USD with 1 standard lot at the current market price of 1.2100/1.2102. Following will be the exposure amount in a short position.
$1.2100 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,100
(bid price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went down by 150 pips and reaches 1.1950/1.1952. By closing the position at this position, the following will be the profit.
$12,100 – $(1.1952 * 100,000 * 1/10) = $12,100 – $11,952 = $148
exposure – (ask price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) = profit
It must be noted the exposure amount ($12,102 in the long position example and $12,100 in the short position example) will be at risk of capital markets. If the leverage is high, the profit/loss amount will move more with the change in the pip value of the underlying asset.
Chapter #3
How Online Forex Trading Works
Online trading is a platform retail investors use to trade forex. Brokers who connect traders to liquidity providers (e.g. commercial banks) offer these platforms. Retail investors get to invest in the market via derivatives or OTC instruments such as CFDs on these platforms. Low deposit is not a barrier in online trading. Brokers offer margin-based trading allowing traders to leverage.
Online trading has become popular with the advent of technology. MT4 and MT5 are the most popular trading platforms. All you need to trade on these platforms is a brokerage account and a minimum deposit as stipulated by your broker. Once this is done, you are ready to trade. Institutional traders use platforms like Refinitiv.
3 ways to trade forex
There are three main ways to trade in foreign exchange: spot, forward, and future.
Spot market
The spot market is also known as the ‘cash market,’ where currencies are bought and sold and delivered on the spot. The price of a currency in the spot market is determined by demand and supply. That means the more the demand for a currency higher the value of that currency.
However, it’s not that simple. Some countries intentionally keep the currency values low to make export cheaper or attract foreign investments. The currency value is calculated on many factors, such as interest rate, market sentiment, political change, and economic news.
The final deal between one party that sells an agreed-upon currency price and the other that buys that agreed-upon exchange rate is known as a ‘spot deal.’ Once you close the position, you receive the specified amount of that currency in cash. Although the spot deal is considered spontaneous, the cash settlement usually takes two days.
Forward market
A private agreement between the two parties to buy a currency at a future date and the pre-agreed price is a forward contract. Let’s take an example to understand how a forward contract works.
Assume that a UK car company wants to secure a contract for a future purchase of spare parts from X, which is located in the US. The UK company signs an agreement with the US company to buy the spare parts after six months.
Both agree for a future exchange rate of 1 GBP = 1.3700 USD, and at the time of the agreement, 1 GBP is equal to USD 1.3700. Now suppose, after six months, the value of one dollar drops to 1.3800. That means the importer will benefit by USD 0.01 per unit of the exchanged currency. Now reverse the situation, the price of one dollar increases to 1.36.
In this case, company X (exporter) will benefit from the forward contract to hedge their risk. The vital thing to note is that currency value can move in any direction, either up or down. Who benefits from a forward contract depends upon the value of one currency against the other after six months.
Future market
A future agreement is similar to a forward contract; the only difference is that latter is a standardized contract. The futures contract is a standard contract that specifies the quantity of a particular asset at a pre-determined price and delivery date.
For example, suppose Indian Oil signs a future contract to import 1 million barrels of oil with an oil producer based in Saudi Arabia. The oil producer promises to deliver the specified quantity in twelve months at a pre-agreed price of $75 per barrel.
So even when the price of one barrel falls to $70, the importer is obligated to pay the premium. The same is true when the price reaches $80; the oil producer will deliver the quantity despite the changes in the spot price.
Basic Forex Trading Terminologies
Forex trading terms are quite many. However, you do not have to learn all at once. Here are some basic terms you should know:
1) Pips: A pip shows the unit change in the value between two currencies. A pip measures this change whether there is an increase or decrease in value. Here is an example to help you understand.
Let us say GBP/USD moves from 1.3361 to 1.3362. This means that the dollar rose in value by 0.0001, which equals one pip. Conversely, if GBPUSD moves from 1.3361 to 1.3359, then the dollar fell in value by 0.0002, which equals two pips. Pips are key to knowing how much you stand to gain or lose in a trade.
2) Currency Pairs: As stated earlier, currencies are traded in pairs on the forex market. You are buying a currency and selling another simultaneously. This is why currencies are paired against each other. A currency pair typically contains six letters. Let us work through this.
- GBP is a single currency that represents the Great Britain Pound.
- USD is a single currency that represents the U.S. Dollar.
- When paired together you have GBP/USD. This is a currency pair.
- In GBP/USD currency pair, GBP is the base currency while USD is the quote currency
- Buying the GBP/USD pair means buying GBP in return of USD
- Selling GBP/USD means selling GBP in return for USD
- On a brokers’ platform, currency pairs are quoted as – GBPUSD.
A currency pair could be major, minor, or exotic, depending on its makeup.
3) Leverage: Leverage is your broker borrowing your money to trade. If you do not have enough money to open a certain position size, your broker takes a down payment from your deposit and lends you the rest. This down payment is known as the margin. When you close the position, the margin is returned to your deposit. Leverage is usually expressed in ratios.
Here is an example, Assuming you want to open a $5000 position in the market. Your broker can take a margin of $500 from your deposit. Your leverage, in this case, is 10:1 ($5000/$500 =10/1). This is the power of leverage. You get to use a small volume of money to control a huge volume of money.
4) Bid and Ask Prices: Your broker gives you these two prices for a currency pair. The bid price is the highest price your broker can buy a currency from you. The ask price is the lowest price your broker can sell a currency to you. The ask price is usually higher than the bid price.
5) Spread: The spread is the difference between the speed and the ask price. The spread is also measured in pips.
6) Lot Sizes: Lot size tells you the specific amount of a currency you want to buy or sell. Just like you go to the market to buy things with specific numbers, it is with forex trading. There are three types of lot sizes. The lot size you trade with determines the unit of a currency you are buying or selling.
Market Trading Terms
Some terminologies are based on market activities and traders must acknowledge these to understand price movements in the forex market.
1. Bull Market
Bullish trend or bullish market is a commonly used term in financial markets to denote appreciation in the price of the asset. For example, a continuous rise in prices of a commodity or stock for a prolonged period will be called a bullish trend.
In a forex pair, a bullish trend can be due to appreciation as well as the depreciation of one currency with respect to other. For example, a bullish trend in EUR/USD currency pair represents an appreciation of EUR and/or depreciation of USD.
2. Bear Market
A bearish trend or bearish market is exactly the opposite of a bullish trend. Continuous depreciation in the price of an asset is commonly denoted as a bearish trend.
In the forex market, appreciation of quote currency and/or depreciation of base currency can be called a bearish trend on a currency pair.
3. GDP
GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value of all the goods and services produced in a country in a particular time period. It is a popular indicator that represents the overall health of a nation’s economy.
Growth in GDP can be compared with other nations to predict the increase or decrease in the price of a currency pair. For example, in a hypothetical currency pair ABC/XYZ, the GDP of the country with ABC currency increases more than the GDP of XYZ nation. This means ABC is growing faster than XYZ and the price of ABC in terms of XYZ is very likely to increase.
4. Inflation
Inflation means a rise in prices in a nation over a time period. There are multiple factors in an economy that can increase or reduce inflation.
Each country has different inflation rates at a particular time interval. One of the primary ways in which inflation is controlled is through the interest rate which is controlled by the Central Bank of the country. This interest rate can be increased to reduce money supply in the market which reduces inflation. However, higher interest rates may hamper GDP growth in an economy which is why Central Banks only use this tool very sparingly.
Inflation rates of two currencies involved in a currency pair can be compared to predict the price movement of a currency pair. The country with a higher rate of inflation will lose its value against the one that has a lower inflation rate.
5. Interest Rates
The interest rate of a country that is also known as the repo rate is the basic rate at which the central bank will provide loans in a particular nation to commercial banks. Interest rates also depict the rate at which investors can earn through fixed deposits in the country.
Interest rates are decided by the central bank or the monetary authority of a nation. Interest rates can be comprehended to predict the price movements in a currency pair.
Trading without strategy is like sailing without a compass. The sailor has no idea about the wind speed or the direction. That’s why the practice of forex analysis plays a vital role in currency trading. You look at the changes in the values of currency pairs and the forces that are influencing those price movements.
Traders use both fundamental and technical analysis for creating a profitable strategy. Many expert traders combine both techniques to take a hybrid approach. In short, the knowledge of technical analysis will tell you when (to buy or sell) and fundamental analysis tells you why (the price movements). Both are indispensable weapons for a successful forex trader.
Let’s deconstruct both methods one by one.
Fundamental Analysis
What economic factors will impact the demand and supply of a currency? Welcome to Macroeconomics 101, the law of demand and supply. If the demand for a currency is increasing, the trader may assume the prices will rise. On the other hand, a demand reduction may be an indication of an eventual fall.
However, it’s not that simple! There are many factors such as economic health, political stability, global events, and others that influence the expansion and contraction of a particular currency. For instance, the US Sub-Prime Lending Crisis in 2008 caused a massive breakdown of financial systems worldwide.
The fundamental analysis generally involves the following economic indicators:
1. Economy:
In addition to global economic events, the localized changes in a national economy can also influence the currency prices of that country. For instance, the increased commodity prices globally can strengthen Australian dollars.
2. Political Changes:
Although government changes are not a frequent affair, currency prices can be affected during a transition period. Developed countries have relatively stable regimes in comparison to developing countries. Political instability is the main reason why the currencies of many African countries are so unpredictable.
3. Monetary and Fiscal Policy:
Central banks use monetary policy as an effective tool to control the demand and supply of a currency. They can reduce the interest rate in an economic slowdown and can increase to curb the inflation caused by economic growth. The fiscal policy entails taxation and government spending. Higher taxes can drive slower credit and economic development. Both government policies can have a significant impact on the national currency.
4. Activities of Major Participants:
Main participants such as banks, financial institutions, or hedge funds may buy or sell a specific currency to up or down the prices. You will be in much better positions if you have an idea about the main speculators of the forex market.
5. Economic data and reports:
Main participants such as banks, financial institutions, or hedge funds may buy or World governments publish statistical data and reports that reveal the economic health and performance over a period. Many financial reports like employment data, inflation rate, GDP, and foreign exchange reserve can indicate regional economic conditions, which can dramatically impact the local currency. A forex dealer can use an economic calendar to avoid unwanted surprises from the release of new data.
Technical Analysis
Charts and graphs are the primary tools of technical analysis. Charts help traders identify historical performance, ongoing trends, and price movements and calculate risk to maximize gains from currency trading.
Understanding different charting formats such as line, bar chart, and candlestick is essential to develop a solid trading strategy for beginners. The following are important terminologies associated with technical analysis.
1. Bar chart:
It is the most basic charting which helps users select a currency and its performance for a fixed period. The bar chart shows the highest and lowest currency price points and average performance over the period chosen.
2. Candlestick:
It also displays the same information: open, low, high, and close. However, the representation of data is very different from the bar chart. It becomes easier for users to see the highest and lowest peaks of the currency movements with thin vertical lines.
3. Price Trends:
Trend is a term used in technical analysis of capital markets that depicts the direction of the price. Generally, the price of the underlying instrument moves in a particular direction until a trend reversal is witnessed. The tops and bottoms of the charts can be analysed to identify the price trend at a given time.
Trendlines and trend reversal are very important components of technical analysis. A higher-high price action followed by a higher low represents an uptrend (bullish) while a lower low and lower high depict a downtrend in price movement.
4. Support and Resistance
Support and resistance are the prices at which the trends are likely to reverse or stop moving further in that direction. There can be multiple support and resistance levels for a single financial instrument.
Support is the lower limit at which the price trend is likely to reverse or stop moving further below. Resistance is the upper limit on the price trend. Whenever a resistance or support level is broken, the price moves significantly. These limits are created due to trend reversals and stagnancy of prices at the price that same particular level. A support or resistance level gets stronger every time it resists the price movement.
5. Moving Average
As the name suggests, the moving average is an important indicator that depicts the average price movement in a given time. A moving average indicator creates a series of averages of different subsets of the full data sets of prices in a particular time interval. Current prices below the moving average depict a buying opportunity while the prices above the moving average may benefit the sellers.
6. Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci retracement levels are based on the Fibonacci sequence and are used to identify potential support and resistance levels. Traders use these levels to determine potential price retracement areas during a trend.
7. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of a moving average (typically 20-day SMA) and two standard deviations above and below the moving average. They help traders identify periods of high or low volatility and potential price breakouts.
8. Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick charts display price data in a visual format using candlestick patterns. Traders analyze patterns such as doji, engulfing patterns, and hammers to identify potential trend reversals or continuation.
9. Volume Analysis
Volume analysis examines trading volume accompanying price movements. It helps traders understand the strength or weakness of a price trend and identify potential reversals or breakouts.
10. Chart Patterns
Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, are formed by price movements and can indicate potential trend reversals or continuations.
There are hundreds of strategies that are used in the technical analysis of financial instruments. Technical analysis works well on instruments with high liquidity like the forex market.
Experienced traders often use technical analysis in combination with fundamental analysis to understand why the value of a currency rises or falls for the selected period. For example, if the fundamentals indicate that the US Dollar will strengthen against the Euro due to policy divergence, and the technical analysis also indicates the same, then it is much more likely that your strategy may be successful as compared to incomplete research.
You can use simple mathematical tools such as moving averages, trend lines, and others for technical analysis. You can learn about more advanced concepts like Elliott Wave Theory, Fibonacci Studies, and Pivot Points as you progress.
Chapter #4
How to Trade Forex on your Broker’s Platform
Now, let us put all we have said together. Here is a systematic guide to trading forex on your broker’s platform. Let us say you place a trade to buy 1 micro lot of GBPUSD at an entry price of 1.3327. If the price increases from 1.3327 to 1.3360. The change in price is calculated as 1.3360-1.3327. This gives you 33pips in profit.
In monetary terms your 33 pips is multiplied by the pip value of your lot size. Remember that the value of a micro lot is 10cents. Therefore, your profit is calculated as 33 x 10cents. This gives you 330cents ($3.30). This is how you trade on your broker’s platform and calculate your profits.
Online Forex Trading Platforms in Malaysia
Forex trading is legal in Malaysia. Only institutional traders get to trade forex through local brokers. Since the framework for electronic trading came into effect in November of 2019, institutional investors have been able to trade forex via approved platforms like Bloomberg and Refinitiv. The latter’s Malaysian office is located in Kuala Lumpur according to their website.
Online forex trading is not available to retail investors locally. If you are a retail trader, your only options are foreign brokers. This is where online trading becomes risky.
There are foreign brokers who accept traders from Malaysia. However, this does not mean you can register with any broker.
You should trade with regulated brokers only. If you choose an unregulated broker, you can fall victim to fraudulent business practices. It is important that tier-1 and tier-2 regulators like the FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), and FSCA (South Africa) regulate your broker.
These brokers also offer different accounts with varying instruments, execution speed, and fee. Since Islam forbids earning money via interest, any broker you choose must also offer an Islamic account. Islamic accounts do not incur rollover or swap charges for holding a trading position overnight.
Many brokers offer Islamic or swap free account which does not incur rollover charges. These charges are revenue for the broker. If it is not charged then traders might need to pay additional commission or increased spread. Clients must inquire the broker about the consequences of choosing Islamic account before choosing a broker in Malaysia.
You also do not need much money to begin trading at a retail level. Some brokers allow a minimum deposit of $5 to open a trading account. This allows you to open an account on a budget.
There are many tier-1 regulated brokers accepting Malaysian clients. These brokers allow you to deposit through local banks and offer swap-free Islamic trading accounts. Such brokers include AvaTrade, FXTM, XM Trading, Tickmill, OctaFX, and HotForex.
(Please note that the brokers listed above are not the only ones accepting Malaysian clients).
XM Trading and HotForex allow a minimum deposit of $5. FXTM’s minimum deposit is $10 while OctaFX minimum deposit is 25$ Tickmill, and AvaTrade require a minimum deposit of $100. Another important thing to know about your broker is their fees. These fees are charged based on the account type you choose to open with them. You should choose an account that matches your risk appetite and your budget.
How can you Trade Forex Online in Malaysia?
The first step to trading forex online is to open an account with a broker. Here are the basics of doing this.
1) Compare forex brokers: Brokers are not the same. Even if you have a number of brokers that offer an Islamic account, you still have to do your research. Research and compare your brokers along these lines.
- Regulation: The issue of regulation cannot be overemphasized. Your broker must be regulated with tier-1 or tier-2 regulatory authorities. The FCA, ASIC, CySEC, and FSCA are trustworthy regulators.
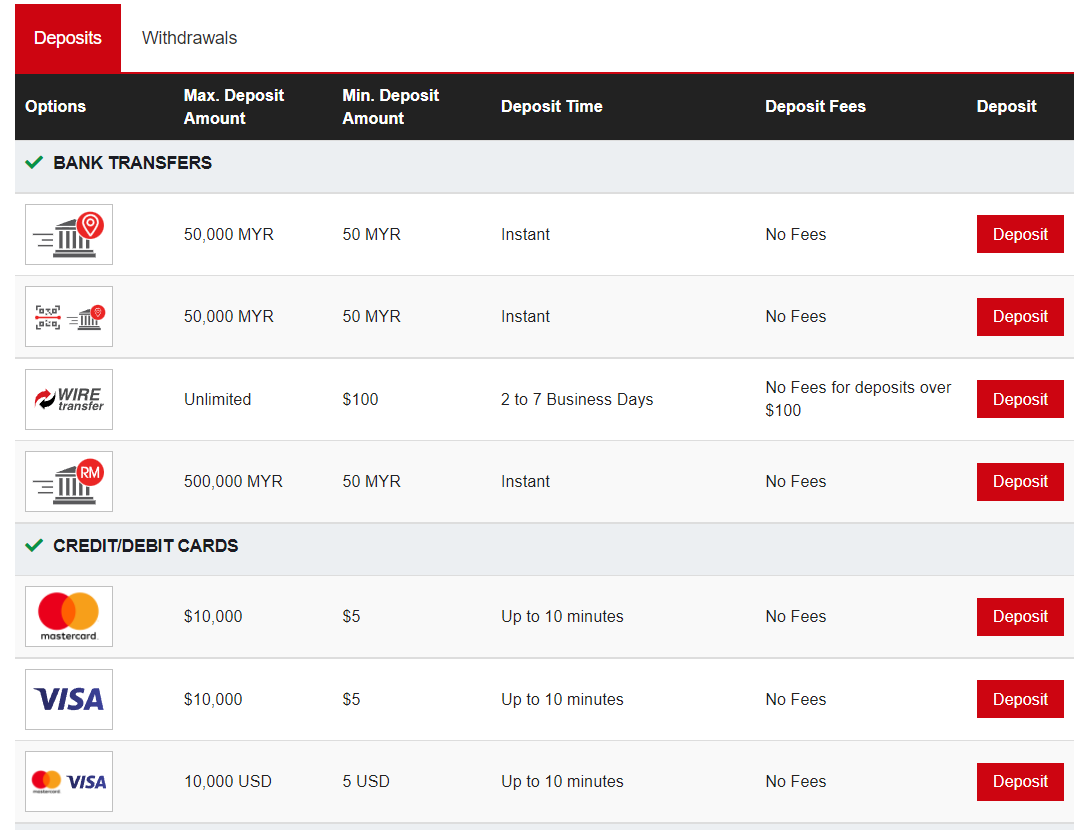
- Deposit methods: Any broker you choose must make a deposit of funds easy. You should be able to deposit in your local currency.
- Instruments: An instrument simply means a tradeable asset. Your broker should offer you a range of instruments. Currency pairs, commodities, metals, and CFDs are instruments you should look out for on your broker’s platform.
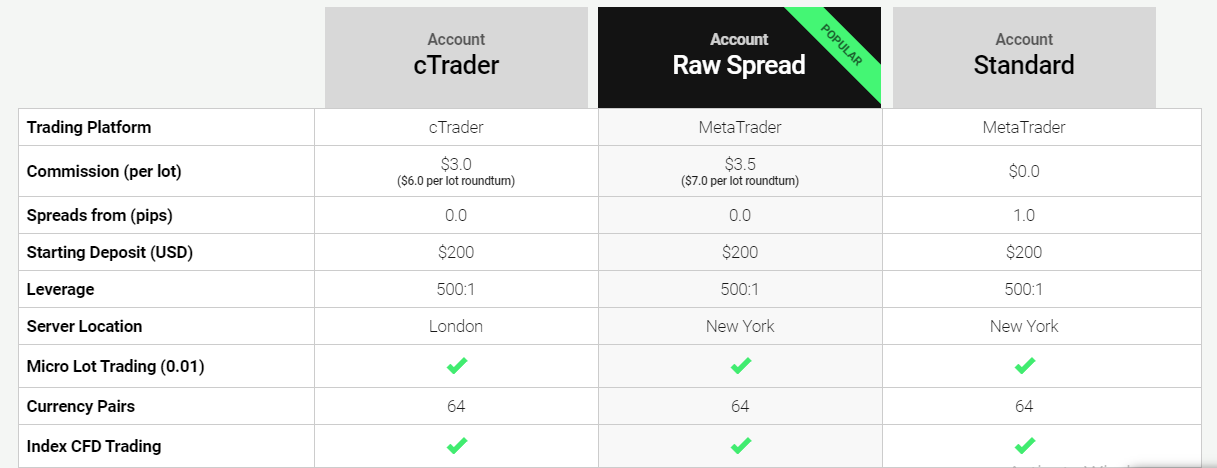
- Account types: The type of account you open determines the instruments you can trade, the fees you are charged, and the execution of your trade. Browse through the different accounts your broker offers. You get acquainted with the trading conditions in those accounts when you do this.

You can find all you need to know about brokers on their website. Do your due diligence before selecting a broker.
2) Register: After choosing a broker, the next step is to register with them and pick an account type that pleases you.
3) KYC Documentation: Your broker will require two documents to verify your identity. You will be required to submit an ID document and a proof of address document. Once these documents are verified, you can proceed to the next step.
4) Deposit your funds: After account verification, you need to deposit or add funds to your account.
5) Download Trading Platform: Now you need to download your broker’s trading platform and begin your trading journey.
New traders are advised to demo trade for some time. This helps you back-test your strategy and build confidence.
Steps to Open a Forex Trading Account in Malaysia
The account opening process at every regulated broker is nearly similar. However, the process and time required to open the live account can vary from broker to broker. Following are the steps to open a live trading account in Malaysia.
Step 1: Select a Broker
Traders must check and compare every aspect of the broker and choose the most suitable broker with regulations, low fees, availability of desired instruments, helpful customer support service, convenient deposit and withdrawals, and a user-friendly trading platform.
Step 2: Visit their Website or Download the App
After choosing the broker, you need to visit their official website or download the application to open the account.
Step 3: Enter Basic Details
The first signup process involves providing basic details like name, phone number, email, and country of residence. Some brokers may ask for a few more details.
Step 4: Select Account Type
Most forex and CFD brokers offer more than one account type with different pricing structures, trading platforms, or trading conditions. Traders must choose the most suitable account type while opening their accounts.
Step 5: Document Verification
After configuring the account and answering a few basic questions related to forex trading, traders are required to verify their documents by uploading soft copies. Brokers will ask for name and address proof which can be done with a passport, national identification document, etc. Each broker can take different times to verify the document ranging from 2 hours to 24 hours on business days.
Step 6: Deposit Funds
Once the account has been verified, clients can deposit funds through the accepted methods from the website or application of the broker. It is important to check the associated fees and time required to process the transaction.
Step 7: Download the Trading Platform and Start Trading
Once the deposits are visible in the account equity, you can open trading positions on available instruments through the trading platform. The trading platform can be downloaded on mobile and desktop devices and can also be accessed through the web.
Examples of Forex Trading with Leverage
Example 1) Assume you have $4000 in your account with a 50:1 leverage. This means you can trade up to $200,000 in the market.
You placed a trade order to buy a standard lot of EURUSD at 1.2800. Without leverage, you will need $128,000 to buy 100,000 units of EUR. However, the leverage of 1:50 only requires you to have a marginal amount of 1/50 or 2% of this, i.e $2560 in your account.
On this trade you expect the EUR to rise against the USD. A pip in this trade is worth $10. It must be noted that we have ignored spread in this example which means the bid price will be the same as the ask price.
You also set your take profit at 100 pips from 1.2800, which is 1.2900, and a stop loss of 50pips, which is 1.2750. If this trade goes your way, your 100 pips profit gives a $1000 profit (100pips x $10). If you are wrong, you lose $500 (50 pips x $10).
If you took this trade without any leverage, you could only buy $4000 worth of EUR units (3125 or 0.03 lot at the rate of 1.28). A movement of 1 pip would have moved your profits/loss by $0.03. 100 pips profit would be $3 profit.
Example 2) Assume you have a $5000 account with 50:1 leverage. You chose to sell a standard lot of GBPUSD at 1.3900. This means you are speculating a fall of the GBP against the USD. For this, you will need to have (1.3900 x 100,000 / 50) = $2780 in your account.
You intend to bag 300 pips here, so you set your stop loss a 100 pips from your entry at 1.4000. Your trade was going well until a fundamental event triggered your stop loss. Since a pip in this trade is valued at $10. Your loss will be a whopping $1000 (100 pips x $10). You just lost 20% of your account in a single trade.
Now let’s move to a hypothetical situation where you took this trade without leverage. You’d have purchased 0.03 standard lot of GBPUSD. A pip will be worth 3 cents this time. Your 100-pip loss would have been a paltry $3. Leveraging this trade gave you much higher loss.
Example 3) Now let’s take another example of a loss trade with leverage of 1:100 and spread of 2 pips. For easier understanding, the spread wasn’t considered in the above examples as the bid and ask prices were the same.
Suppose EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.2800/1.2802. This means that 1 unit of EUR will be bought at 1.2082 while the same will be sold at 1.2800. Suppose, you opened a long position with the standard lot hoping for a price increase at 1.2802. The ask price (higher) will be applicable in case of opening a long position.
With the leverage ratio of 1:100, you will need to have a minimum $1280.2 in your account to open a position of 1 standard lot. With $1280.2 in your account you are buying 100,000 units of EUR.
After a few minutes, the price goes down by 20 pips to 1.2780/1.2782. Now if you wish to close this position the bid price (lower) will be applicable to close the trade. You bought EUR in return for USD and now you need to sell the EUR back to receive USD and close the trade.
The price for a standard lot of EUR/USD moved down by 20 pips but there was also a spread of 2 pips. Hence, the overall loss will be 22 pips. The loss for 1 pip is 10$ on a trade of a standard lot so in this case, the overall loss will be $220.
This is why it is popularly said that leverage is a double-edged sword. It can allow traders to open bigger positions with smaller deposit amounts. Hence, profits, as well as loss amount, will increase with an increase in the leverage ratio.
You need only three things to trade forex:
- A good PC or mobile phone.
- A stable internet connection.
- A trading platform. It could be web, mobile or integrated.





